PVD | Preloading and Vertical Drains
Preloading and Vertical Drains (PVD) is a common soil improvement technique used to accelerate the consolidation process and increase the shear strength of soft, compressible soils, such as clays and silts. Here’s an overview of how it works and its benefits:
Principles of PVD Soil Improvement
1. Preloading
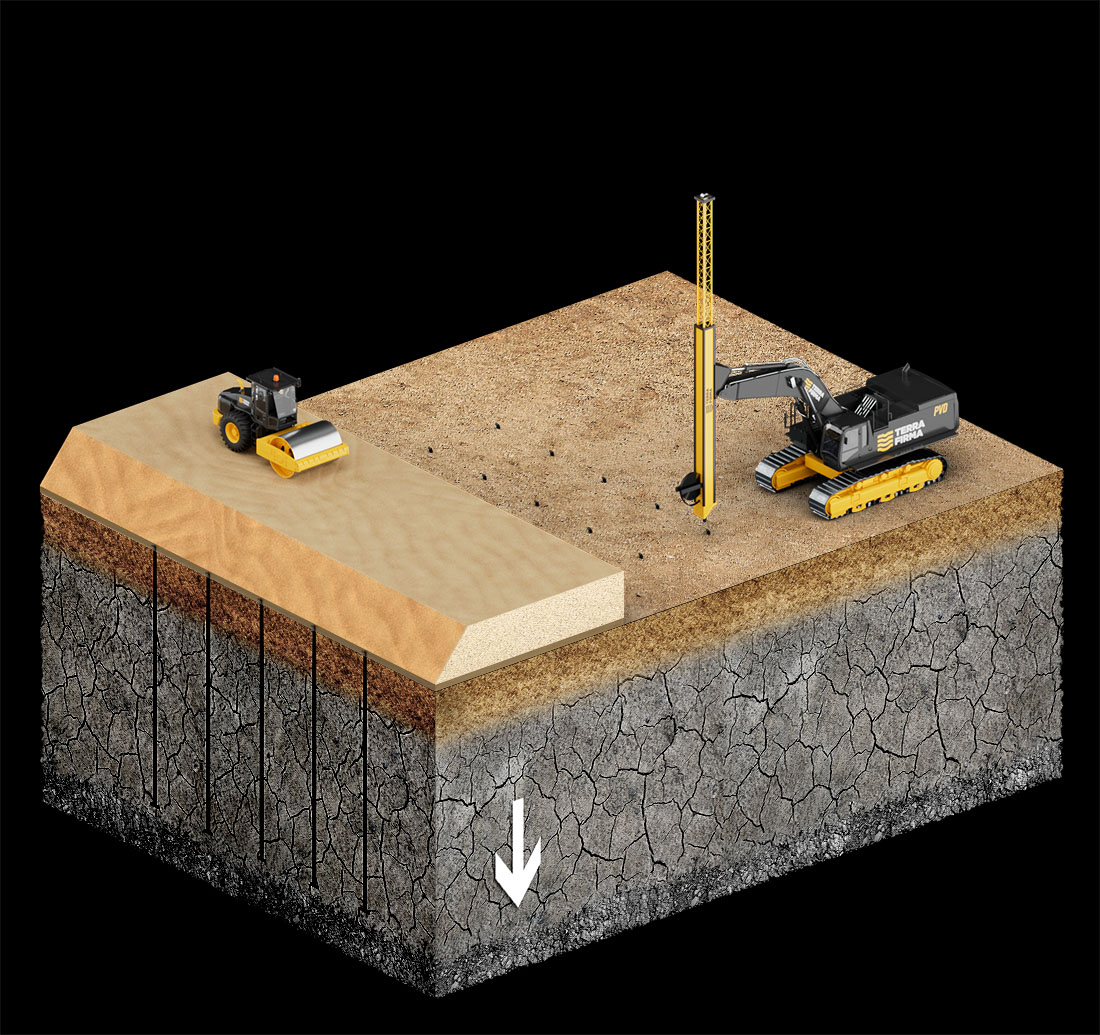
- Loading the soil: Applying a temporary surcharge load (e.g., soil or water) on the ground surface.
- Purpose: To compress and consolidate the underlying soft soil layers by expelling pore water, thus increasing soil strength and reducing future settlement.
2. Vertical Drains (PVDs)
- Installation: Vertical drains, typically made of prefabricated synthetic materials, are installed into the ground at regular intervals.
- Function: They provide a shorter path for water to escape, enhancing the consolidation process.
- Types: Common types include sand drains, wick drains, and prefabricated vertical drains (PVDs).
Procedure
1. Site Preparation
- Clear and level the site.
- Install vertical drains using specialized equipment (e.g., mandrels, vibratory hammers).
2. Preloading
- Place the surcharge load on the ground surface.
- Maintain the load for a specified period, allowing time for water to drain and soil to consolidate.
3. Monitoring
- Regularly monitor settlement, pore pressure, and other relevant parameters.
- Adjust the surcharge load as necessary.
4. Removal
- Once the desired level of consolidation is achieved, remove the surcharge load.
Benefits
- Accelerated Consolidation: Significantly reduces the time required for soil consolidation compared to natural processes.
- Reduced Settlements: Helps achieve the required level of settlement before construction begins, ensuring stability.
- Increased Bearing Capacity: Improves the soil’s bearing capacity, making it more suitable for supporting structures.
- Cost-Effective: Often more economical compared to other deep foundation solutions, such as piling.
Applications
- Construction Projects: Used in construction of embankments, highways, railways, airports, and building foundations.
- Land Reclamation: Helps stabilize reclaimed land by improving soil properties.
- Dewatering: Effective in dewatering soft soils in coastal and low-lying areas.
Limitations
- Installation Challenges: Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Effectiveness: Depends on soil type, depth, and the characteristics of the surcharge load.
- Environmental Concerns: May cause ground subsidence and affect groundwater flow patterns.
PVD soil improvement is a versatile and effective technique, especially beneficial in areas with soft, compressible soils requiring rapid and substantial improvement in soil properties.











Insert code: <i rel="code">Put code here</i> or <i rel="pre">Put code here</i>
Insert image: <i rel="image">Put Url/Link here</i>
Insert title: <b rel="h3">Your title.</b>
Insert blockquote: <b rel="quote">Put text here</b>
Bold font: <b>Put text here</b>
Italics: <i>Put text here</i>
0 Comments